1798 W H Hall Large Antique Print of the Apparatus of The Microscope, Lenses
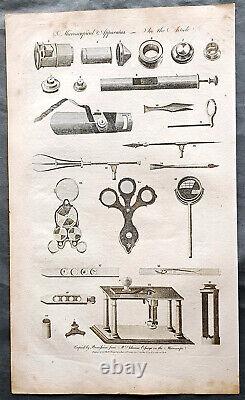

15in x 9in (380mm x 230mm). This large original copper-plate engraved antique print was published by William Henry Hall in the 1798 edition of The new royal encyclopedia; or, complete modern universal dictionary of arts and sciences on a new and improved plan.... Printed by Charles Cooke, London. Paper thickness and quality: - Heavy and stable Paper color : - off white Age of map color: - Colors used: - General color appearance: - Paper size: - 15in x 9in (380mm x 230mm) Plate size: - 15in x 9in (380mm x 230mm) Margins: - Min 1/2in (12mm).
Margins: - Age toning Plate area: - Age toning Verso: - Age toning. Background: Although objects resembling lenses date back 4000 years and there are Greek accounts of the optical properties of water-filled spheres (5th century BC) followed by many centuries of writings on optics, the earliest known use of simple microscopes (magnifying glasses) dates back to the widespread use of lenses in eyeglasses in the 13th century. The earliest known examples of compound microscopes, which combine an objective lens near the specimen with an eyepiece to view a real image, appeared in Europe around 1620. The inventor is unknown although many claims have been made over the years. Several revolve around the spectacle-making centers in the Netherlands including claims it was invented in 1590 by Zacharias Janssen (claim made by his son) and/or Zacharias father, Hans Martens, claims it was invented by their neighbor and rival spectacle maker, Hans Lippershey (who applied for the first telescope patent in 1608) and claims it was invented by expatriate Cornelis Drebbel who was noted to have a version in London in 1619.
Galileo Galilei (also sometimes cited as compound microscope inventor) seems to have found after 1610 that he could close focus his telescope to view small objects and, after seeing a compound microscope built by Drebbel exhibited in Rome in 1624, built his own improved version. Giovanni Faber coined the name microscope for the compound microscope Galileo submitted to the Accademia dei Lincei in 1625 (Galileo had called it the occhiolino or little eye). The first detailed account of the microscopic anatomy of organic tissue based on the use of a microscope did not appear until 1644, in Giambattista Odiernas Locchio della mosca, or The Flys Eye. The microscope was still largely a novelty until the 1660s and 1670s when naturalists in Italy, the Netherlands and England began using them to study biology.Italian scientist Marcello Malpighi, called the father of histology by some historians of biology, began his analysis of biological structures with the lungs. Robert Hookes Micrographia had a huge impact, largely because of its impressive illustrations. A significant contribution came from Antonie van Leeuwenhoek who achieved up to 300 times magnification using a simple single lens microscope. He sandwiched a very small glass ball lens between the holes in two metal plates riveted together, and with an adjustable-by-screws needle attached to mount the specimen. Then, Van Leeuwenhoek re-discovered red blood cells (after Jan Swammerdam) and spermatozoa, and helped popularise the use of microscopes to view biological ultrastructure.
On 9 October 1676, van Leeuwenhoek reported the discovery of micro-organisms. The performance of a light microscope depends on the quality and correct use of the condensor lens system to focus light on the specimen and the objective lens to capture the light from the specimen and form an image.
Early instruments were limited until this principle was fully appreciated and developed from the late 19th to very early 20th century, and until electric lamps were available as light sources. In 1893 August Köhler developed a key principle of sample illumination, Köhler illumination, which is central to achieving the theoretical limits of resolution for the light microscope. This method of sample illumination produces even lighting and overcomes the limited contrast and resolution imposed by early techniques of sample illumination. Further developments in sample illumination came from the discovery of phase contrast by Frits Zernike in 1953, and differential interference contrast illumination by Georges Nomarski in 1955; both of which allow imaging of unstained, transparent samples. Hall, William Henry Hall was responsible for a significant publication in the middle of the 18th century The new royal encyclopedia; or, complete modern universal dictionary of arts and sciences on a new and improved plan.
Containing a digest and display of the whole theory and practice of the liberal and mechanical arts comprising a general repository of ancient and modern literature. Including all the material information that is contained in Chamber s Cyclopedia, the Encyclopædia Britannica, and the French Encyclopædie. First published in 1788 going into many re-issues over the next 50 years. The three volume set contained 153 copper-plate prints and maps, including some folding maps.
Contained many brief encyclopedic entries in alphabetical orders plus longer, mainly illustrated, sections (systems or treatises) on a variety of subjects: Aerology; Aerostation (hot air balloons); Agriculture; Algebra; Amphibiology; Anatomy; Annuities; Architecture; Arithmetic; Astronomy (includes plates of telescopes); Book-Keeping; Botany; Brewing; Chronology; Chymistry; Comparative Anatomy; Concology; Dialling; Distillation; Drawing; Earth; Earthquakes; Electricity; Entomology; Farriery; Fencing; Fluxions; Fortification; Gardening; Geography (this section includes six folding maps); Geometry; Globes; Grammar; Heraldry; Hydrostatics and Hydraulics (one plate included a diving bell); Icthyology; Knighthood; Logic; Mammalia (included a plate showing whales); Mechanics; Medicine; Mensuration and Gauging; Miscroscopic Apparatus (microscopes); Midwifery; Military Affairs; Music; Natural History; Naval Affairs; Navigation (includes a folding map showing Cooks voyages); Optics; Oratory; Ornithology; Peerage; Perspective; Pneumatics; Projectiles; Steam Engines; Surgery; Surveying; Trigonometry; Vermeology; Volcanos; and War. Hard to find a complete set, as many have been broken up for their handsome copper plate engravings and maps. What is an Antique Map. The word Antique in the traditional sense refers to an item that is more than a hundred years old.
The majority of antique maps for sale today come from books or atlases and have survived due to the protection offered by the hardback covers. The first thing to determine when staring a collection or purchasing an item, is what is important to you. Most collectors prefer to build their collections around a theme. You may decide to collect maps from one region or country, charting its development through time.
Similarly you could collect maps of one particular period in time, by type i. Sea or celestial charts or by cartographer.
The collector might also want to consider the theme of cartographical misconceptions such as California as an island or Australia as Terra Australis or the Great Southern Land. The subject is so wide that any would-be-collector has almost endless possibilities to find his own little niche within the field, and thereby build a rewarding collection. Starting a collection & pricing.
Pricing is based on a number of different factors, the most important of which is regional. In any series of maps the most valuable are usually the World Map and the America/North America. The World because it is usually the most decorative and America because it has the strongest regional market.
Other factors that come into play re: price is rarity, age, size, historical importance, decorative value (colour) and overall condition and quality of paper it is printed on. As specialised dealers, we frequently work with first time map buyers who are just starting their collection. Classical Images was founded 1998 and has built an excellent reputation for supplying high quality original antiquarian maps, historical atlases, antique books and prints. We carry an extensive inventory of antiquarian collectibles from the 15th to 19th century.
Our collection typically includes rare books and decorative antique maps and prints by renowned cartographers, authors and engravers. Specific items not listed may be sourced on request. Classical Images adheres to the Codes of Ethics outlined by the Antiquarian Booksellers Association of America (ABAA). We are a primarily an online based enterprise, however our inventory may be viewed by appointment. This item is in the category "Antiques\Science & Medicine (Pre-1930)\Scientific Instruments\Other Antique Science Equip". The seller is "searching01" and is located in this country: AU. This item can be shipped worldwide.